A 30a circuit breaker can safely carry the exact 30a current but nec suggests 80 as a safe current limit as compared to the rated current.
Motor circuit breaker sizing pec.
Minimum circuit size is 12 with 20 amp cb.
Refer to table 310 16 when selecting the proper size conductor to serve a single motor.
Difference between circuit breaker and isolator disconnector circuit breaker size calculation for continuous non contentious load.
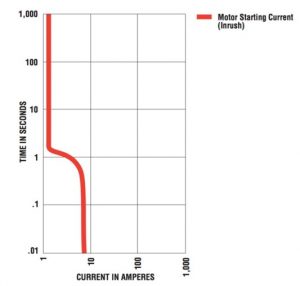
This level of protection requires a well designed true dual element fuse.
Maximum loading of any circuit breaker is 80 of rating for non motor loads with exceptions as noted below.
Circuit breaker size 2.
Neutral conductors supplying balanced loads do not have to be counted.
Electroplating branch circuit conductor sizing 6 69 6 69 1 5 elevator feeder demand factors 6 20 6 20 2 4 fire pumps voltage drop mandatory calculation 6 95 6 95 1 7 fixed electric heating equipment for pipelines and vessels branch circuit sizing 4 27 4 27 1 4 fixed electric space heating equipment branch circuit sizing 4 24 4 24 1 3.
You must select the conductor size from table.
As circuit breakers cbs and overcurrent protection devices ocpd are designed for 100 rated current i e.
If circuit is loaded up to 80 ampacity then 6 phase wires can be put in one conduit.
Branch circuit conductors that serve a single motor must have an ampacity of not less than 125 of the motor s flc as listed in tables 430 147 through 430 150 430 6 a.
Per 430 24 size multiple motor conductors as follows.
The fuse sizing in column 4 for lps rk sp lpn rk sp frs r and frn r fuses provides a degree of motor and circuit overload protection to back up the normal motor overload protective device.
Locate where your motor falls in table 430 52 based on the full load current and motor size.
Size the branch circuit short circuit and ground fault protection device per 240 6 a and 430 52 c 1 ex.
The table will give you the size of the short circuit protection as a percentage of the full load current.
High resistance grounding is a means of limiting ground fault current in electrical systems.
This article will address the history use and recent developments in available high resistance grounding technology used with ungrounded voltage systems.